Everything You Need to Know About Extranet
What is an Extranet?
An organization’s intranet includes an extranet. A network of communication that uses TCP/IP, or the Internet Protocol. Give your company’s intranet-regulated access to your clients, customers, and other companies. In other words, a private network that securely allows authorized third parties access to a company’s internal data and operations without allowing access to the full network. Users require this network’s IDs, passwords, and other authentication methods.
A company’s extranet is a private network that it uses to grant authorized access to business data or activities to partners, customers, and other businesses (such as suppliers, vendors, and partners).
An extranet could be viewed as an extension or component of an organization’s intranet if it takes the form of an externally accessible website or platform. This is because data kept on an extranet is frequently only available on the internal network. Users outside the firm can access information on the extranet, but access is restricted and limited to authorized users only.
Examples:
- An online store can communicate with its suppliers and retailers using an extranet network.
- International firms use an extranet network to handle project information, communicate with other organizations, and manage client information.
- Through the university’s extranet network, students can access an e-learning platform.
Extranet Lockout:
Security teams can protect users via extranet lockout from brute-force attacks on finding a threat. In this situation, Active Directory Federation Services, for instance, can stop malicious users from accessing the extranet. Administrators can retrieve details about lockout events from the security audit log.
How to set up an extranet:
An intranet of an organization is set up as a Virtual Private Network since it is subject to security issues due to the use of the internet to connect external users to it. A VPN helps ensure the security of your network on a shared network, such as the internet. Data is transferred via the internet protocol (IP) and the transmission control protocol (TCP).
When a VPN is utilized, the TCP/IP protocol, which is used to transfer data in the extranet, is given an additional layer of protection, assuring secure transactions based on the Internet Protocol Security Architecture (IPsec) protocol.
An organization may additionally take the next two steps to increase the security of its intranet:
Firewall: It limits access by unauthorized users to the extranet.
Passwords: Additionally, it stops authorized users from viewing the data kept on the server, including company personnel.
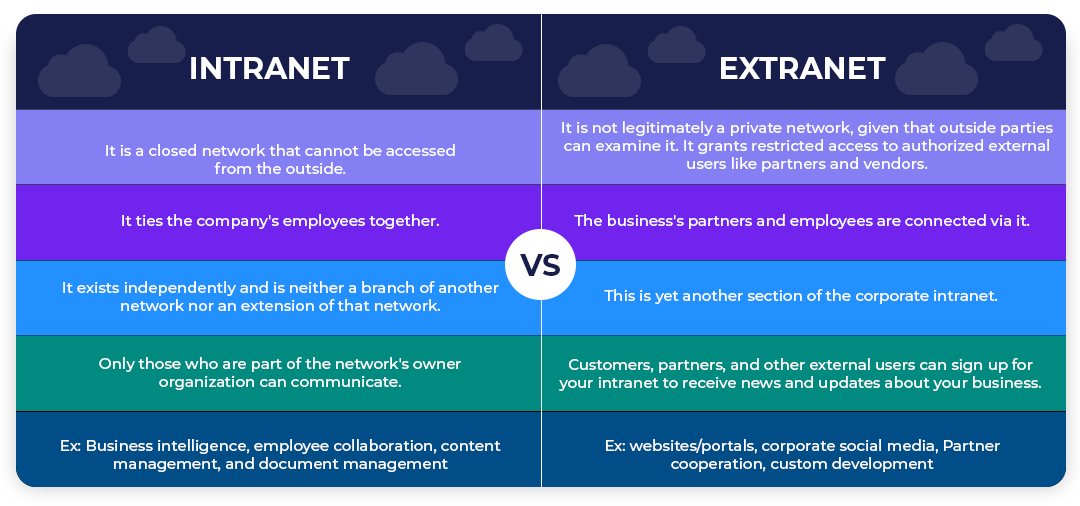
Intranet vs. Extranet:
Extranet Use Cases:
- Electronic data interchange for the exchange of enormous amounts of data.
- Distribute your product catalog just to wholesalers.
- Collaboration with other businesses on collaborative development initiatives.
- Joint creation and application of training initiatives with other businesses.
- The company’s management of online banking services for its affiliated institutions.
- Exclusive communication with partner businesses on matters of mutual interest.
Advantages with Extranet:
Improved engagement and communication: Extranets provide a platform for sharing important information pertinent to all stakeholders, making announcements, or sharing critical updates. This tactic may lead to greater involvement and participation from the personnel and external partners.
Improved efficiency: Startups and businesses of all kinds routinely work together with various outside partners and vendors to develop goods and complete tasks. An extranet can be used to manage these workflows.
Improved collaboration and knowledge sharing: Before introducing well-known team collaboration software like Asana, Trello, and Jira, businesses primarily relied on extranets and intranets to improve communication. This technique made real-time updates and seamless document sharing possible while working with a confidential project or business data in a secure environment.
Disadvantages with Extranet:
Invest: Creating and maintaining an extranet may require a lot of time and resources. The cost includes the price of on-premises hardware and software and the wages paid to information technology staff who create and maintain it. A business that needs more resources to develop and manage an extranet may not find it the best option. Some of these upfront expenditures may be reduced for extranets that are run or hosted in the cloud, such as Microsoft SharePoint.
Security to Data: When using an extranet, security measures must be taken. Unauthorized individuals may access sensitive data if security measures are insufficient. This could lead to the loss of confidential knowledge and competitive advantage. Therefore, internal specialists who can lessen the risk of data leakage are best suited to maintain extranets.
Dependency: The Intranet is necessary for outsiders since they cannot get information otherwise.
Less Interaction: When there is a less face-to-face interaction between customers, business partners, suppliers, etc., relationship building suffers.
Key Issues to Consider:
Remember this after granting trading partners access to your company’s data. What they anticipate it to be is:
- Available
- Most Recent
- Constantly safe
The usability and security of an extranet are key factors in determining its success. Extranet users should be specifically identified, and access should be restricted using rigorous authentication processes and security measures.
Large resources are also required to keep the content of the extranet accurate and current.






